AI’s Impact on Employment
In five years, AI will result in 83 million “structural” job losses, according to the WEF
The unemployment rate has been increasing at a large rate for the past few years or months.
Millions of workers are being laid off. Due to this the rate of unemployment has become very large. Unemployment is the biggest crisis facing the world today. And unemployment will continue to be the biggest crisis in the world for the time to come. World economic corona Some researchers like Institute has just done some survey. What this survey says. We will see it here now.

AI is Creating Unemployment
According to the World Economic Forum’s new Future of Jobs research, structural labor market churn brought on by AI and other economic forces will result in 83 million job losses over the next five years. In the next five years, 44% of employees’ skills will be disrupted, according to WEF, which suggests in its 296-page research that “generative AI models are likely to continue shaping sectoral shifts in employment.”
In five years, AI will result in 83 million “structural” job losses, according to the WEF
The CIOs and other corporate participants to the survey evaluated the demand for analytical abilities as developing most swiftly in terms of skills, despite the growth of “intelligent” technologies driven by AI, “reflecting the increasing importance of complex problem-solving in the workplace.” Tech literacy and innovative thinking came next. The publication of the paper comes shortly after Goldman Sachs analysts warned that “a new wave of AI systems [and] shifts in workflows triggered by these advances could expose the equivalent of 300 million full-time jobs to automation.”
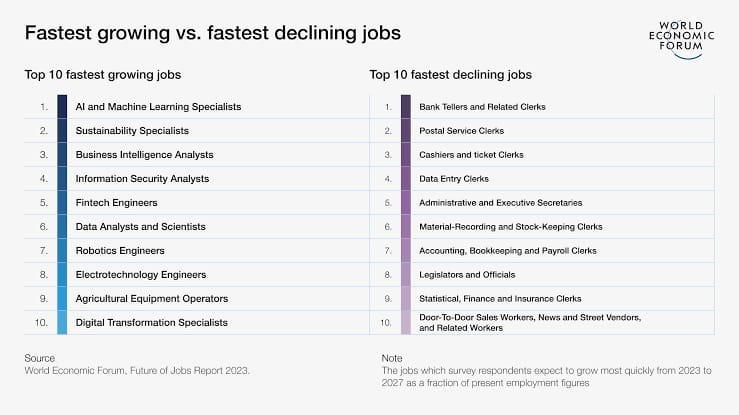
AI Job Losses/Disruption to Drive Significant Shifts in the Labor Market According to the WEF, job losses due to automation and other changes in agricultural technologies and digital platforms “are all expected to result in significant labor-market disruption” and that “the fastest-declining roles relative to their size today are driven by technology and digitalization,” According to the research, clerical and secretarial positions are those that are swiftly disappearing. Traditional back-office positions are being rapidly mechanized as a result of the development of AI. This week’s instance is IBM, where the CEO

26,000 personnel are employed in back-office tasks. “Over a five-year period, I could easily see automation and AI replacing 30% of that.” (IBM added 7,000 new employees in Q1 while eliminating about 5,000 roles this year.) According to the WEF, eight of the top ten industries will have a technology component, and this wider labor market transition will result in the creation of 69 million jobs (for a net loss of 14 million jobs). AI and sustainability will expand the quickest throughout this period. “The biggest drivers of job growth are anticipated to be data analytics, climate change and environmental management technologies, encryption and With COVID-19, geopolitical and economic shifts, and the rapid advancement of AI and other technologies, now risks adding more uncertainty. For people around the world, the past three years have been filled with upheaval and uncertainty for their lives and livelihoods, said Saadia Zahedi, Managing Director, WEF.

The good news is that ensuring resilience has a clear path ahead. Through education, reskilling, and social support systems that can guarantee people are at the Centre of the future of work, governments and corporations must invest in assisting the transition to the jobs of the future, Zahedi continued.
Warning regarding the predictions: According to The Future of Jobs research 2023, tasks are not perceived as being any more automated today than they were three years ago, when the research was first released. Only 1% more activities are mechanized now (34%), compared to the year 2020. Companies surveyed also revised down their predictions for further automation, from 47% of tasks by 2025 to 42% of duties by 2027. In this year’s research, 803 businesses from 45 economies and 27 industrial clusters from throughout the globe, employing more than 11.3 million people, have contributed their thoughts.
